Why SDMX Structural Metadata Governance matters
Statistical organisations face the challenge of effectively managing and integrating vast amounts of data. To ensure clarity, consistency, and efficiency in this process, a well-defined governance framework is essential. SDMX Structural Metadata Governance Framework presents a simplified guideline to facilitate effective data management across an organisation.
SDMX Structural Metadata governance establishes clear processes and responsibilities for maintaining the structure of data and metadata. It allows organisations to achieve harmonisation, making data integration and processing more efficient. By implementing governance principles based on best practices, organisations can enhance their data management practices and improve decision-making processes.
High-quality structural metadata requires a well-defined governance policy that is customised to an organisation’s needs.
I’ve seen that when there is little to no structural metadata governance policy, the usability of statistical data suffers because structures are not shared or harmonised, it is hard to discover, and data managers don’t know who to ask for best practices. To avoid these problems, you need to implement a structural metadata governance policy for your organisation – but how to do so? The answer is in the reference framework for SDMX structural metadata governance that describes a generic governance based on real-world best practices, and provides several adaptions that apply to different institutional needs and settings. David Barraclough, OECD, Manager of SDMX and Data Modelling
The reference framework emerged from similar structural metadata governance requirements at the OECD, but also following needs of our Community members National Bank of Belgium (NBB), and National Institute of statistics and economic studies of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (STATEC) during the conceptualisation of modernisation projects. The strong similarities yet distinct differences in the capacity and practices of these organisations clearly showed the need to have an adaptive governance model based on a common underpinning framework. The guidelines also includes the typical implementation steps, an institutional setting (based on the OECD example), a business process, and a mapping to GSPBM and GAMSO.
What are the key components of SDMX Structural Metadata Governance?
-
- Workflows for Change Processes: Clear workflows ensure that proposed changes to the metadata undergo a systematic review and approval process, promoting efficiency and accuracy.
-
- Identifying Relevant Experts: Involving experts who possess the necessary knowledge and expertise is crucial for making informed decisions regarding the structural metadata. Their involvement ensures the metadata accurately represents the data being managed.
-
- Ownership and Accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities help establish ownership and accountability within the governance framework. This separation allows decision-makers to focus on strategic aspects while ensuring effective execution and maintenance.
-
- Tools for Effective Processes: Using appropriate tools, such as review mechanisms and communication channels, enables collaboration and efficient decision-making. These tools facilitate effective metadata management and promote communication within the organisation.
-
- Ownership and Maintenance of Governance Policies: Ensuring the ongoing relevance and effectiveness of governance policies requires clear ownership and maintenance. Regular updates and revisions keep the policies aligned with evolving organisational needs.
-
- Adoption and Communication: The successful implementation of governance policies depends on their adoption throughout the organisation. Communication initiatives and training programs play a vital role in fostering understanding and widespread compliance.
A simplified guideline for SDMX Structural Metadata Governance
To streamline the implementation of SDMX Structural Metadata governance, organisations can follow these steps:
-
- Assess your organisation’s specific needs and resources.
-
- Identify and involve experts who understand the data and can contribute to decision-making processes.
-
- Define clear workflows for proposing and implementing changes to the metadata.
-
- Assign ownership and accountability for different aspects of metadata management.
-
- Utilise appropriate tools to support effective communication, reviews, and decision-making.
-
- Regularly review and update governance policies to ensure their continued relevance.
-
- Communicate the governance policies and provide training to foster understanding and adoption.
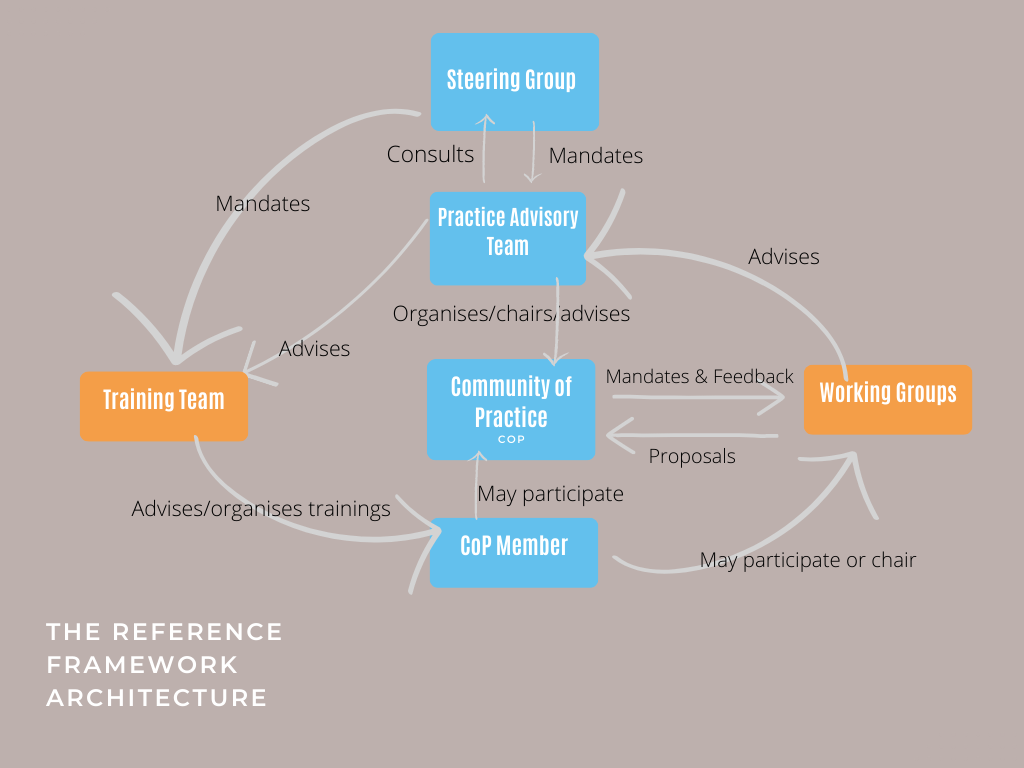
The reference framework architecture
This diagram shows the reference architecture containing all the roles and relationships in this guideline. It can be implemented as is or customised according to each individual organisations’ context.
Conclusion
Implementing a robust governance framework for SDMX Structural Metadata is essential for organisations aiming to enhance their data management practices. By following the simplified guideline organisations can streamline their data integration processes, improve reporting clarity, and achieve more efficient resource management. Embracing SDMX Structural Metadata governance will pave the way for effective decision-making, accurate data representation, and successful navigation of the data-driven landscape.
For more information on the framework, please visit: SDMX-Structural-Metadata-Governance.docx (live.com)
Thank you to David Barraclough Manager of SDMX Data Modelling, Statistics and Data Directorate at the OECD for contributing to this post


